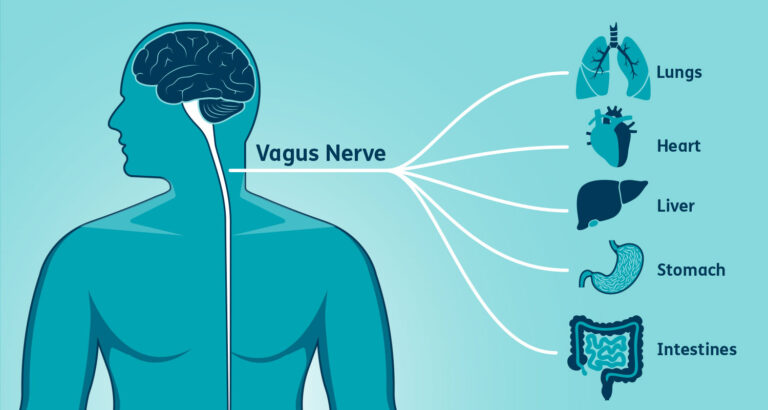
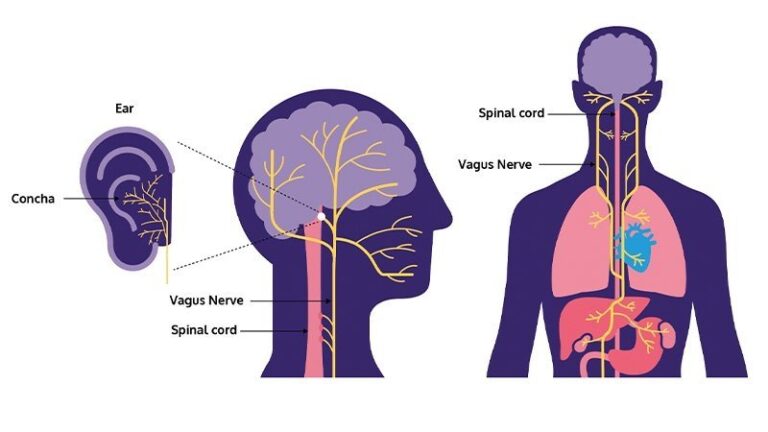
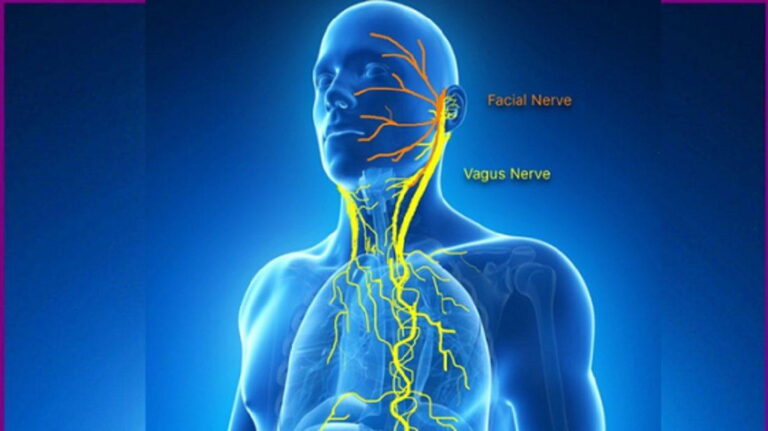
What is H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori)?
Helicobacter pylori is a remarkable bacterium with unique characteristics that set it apart in the realm of gastrointestinal health. Its helical, spiral shape allows it to navigate the protective mucous lining of the stomach, where it establishes a persistent infection. This section will delve into the molecular structure of H. pylori, explaining its helical shape, flagella-driven movement, and the remarkable enzyme urease it produces, which enables it to survive in the acidic environment of the stomach.

What are the Symptoms?
Understanding the symptoms associated with H. pylori infection is critical for early detection and intervention. This section will not only elaborate on common symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea but also delve into less common manifestations such as unexplained weight loss and the presence of blood in the stool. Visual aids will include detailed infographics illustrating the diverse range of symptoms that individuals may experience.
Who is at risk for infection?
Certain populations are more susceptible to H. pylori, and understanding these risk factors is essential for targeted prevention and intervention strategies. This section will explore in detail the demographic factors, such as age and socioeconomic status, living conditions, and lifestyle habits that contribute to an increased risk of infection.
Can H. pylori spread from person to person?
Understanding the modes of transmission is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures. This section will delve into the various ways the bacterium can be transmitted, including close personal contact, shared utensils, and even from parent to child. Visual aids will include educational illustrations depicting the transmission routes, emphasizing the importance of hygiene and sanitation.
What’s the association between H. pylori infection and stomach cancer?
The potential long-term consequences of H. pylori infection are significant, with a noteworthy association with stomach cancer. This section will explore the intricate relationship between chronic infection, inflammation, and the development of gastric malignancies. Visual aids will include detailed diagrams explaining the step-by-step process from infection to cancerous transformation.
When to see a doctor
Recognizing the signs that prompt medical attention is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention. This section will provide a comprehensive guide on when individuals should seek medical advice, considering the severity and persistence of symptoms. Visuals will include flowcharts and timelines to aid in understanding the urgency of seeking professional medical help.
Causes
Delving into the specific mechanisms of how H. pylori infects the stomach lining is essential for understanding its pathogenesis. This section will explore the initial stages of infection, from the bacterium’s entry into the body to its colonization of the gastric mucosa. Visual aids will include detailed animations or diagrams illustrating the molecular interactions involved in H. pylori infection.
How is H. pylori diagnosed? (Diagnosis and Tests)
Accurate diagnosis is pivotal for the effective management of H. pylori infections. Multiple tests are available, each with its strengths and considerations. Understanding these diagnostic methods is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Certainly, let’s dive deeper into the section on diagnosis and tests for H. pylori.
8- How is H. pylori diagnosed? (Diagnosis and Tests)
Accurate diagnosis is pivotal for the effective management of H. pylori infections. Multiple tests are available, each with its strengths and considerations. Understanding these diagnostic methods is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike.
- Blood Tests:
Blood tests are often the initial step in diagnosing H. pylori infection. These tests detect the presence of antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the bacterium. However, it’s important to note that these antibodies may persist even after successful treatment, making blood tests more suitable for initial screening rather than post-treatment confirmation. - Breath Tests:
Breath tests are a non-invasive and reliable method for diagnosing H. pylori infection. Patients consume a substance containing a special type of carbon. If H. pylori is present, it breaks down the substance, releasing a specific carbon compound that is detectable in the patient’s breath. This test is particularly useful for confirming eradication after treatment. - Stool Tests:
Stool tests are employed to detect H. pylori antigens in fecal matter. This method is useful, especially in pediatric cases where obtaining blood samples might be challenging. Stool tests can also be used to confirm eradication post-treatment. Visual aids will include images of stool test kits and the laboratory process. - Endoscopy with Biopsy:
Endoscopy is a more invasive yet highly effective diagnostic method. During endoscopy, a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted into the stomach. Biopsy samples are then collected from the stomach lining for laboratory analysis. This allows for direct visualization of any ulcers or inflammation caused by H. pylori. Visual aids will include images of endoscopic procedures and biopsy collection. - CLO Test (Campylobacter-like Organism Test):
The CLO test is often performed during endoscopy. A biopsy sample is taken, and a small piece of the tissue is placed in a special liquid or gel containing urea. If H. pylori is present, the urea is broken down, producing ammonia and changing the color of the solution. This change in color indicates the presence of H. pylori. - Histology:
Histological examination of biopsy samples allows pathologists to study the stomach lining under a microscope. This provides detailed information about the extent of inflammation, the presence of H. pylori, and any associated changes, such as the development of peptic ulcers or precancerous conditions.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tests:
PCR tests amplify and detect the genetic material of H. pylori. These tests are highly sensitive and can identify the presence of the bacterium even in low concentrations. PCR is particularly useful in cases where traditional methods might yield false negatives.
Understanding the nuances of each diagnostic method is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care. Moreover, patients benefit from being aware of these diagnostic tools, fostering a collaborative approach between individuals and their healthcare providers.
Incorporating visuals in educational materials and discussions about H. pylori diagnosis can enhance patient understanding and engagement. Whether it’s a detailed illustration of the PCR process or a snapshot of an endoscopic procedure, these visuals can bridge the gap between medical jargon and accessible information, empowering individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey.
How does H. pylori infection cause damage?
Understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms through which infection causes damage to the stomach lining is crucial for comprehending the progression of the infection. This section will provide an in-depth exploration of the inflammatory response, secretion of virulence factors, and the disruption of the mucosal barrier. Visual aids will include detailed cellular and molecular graphics.
How is H. pylori treated?
Treatment strategies involve a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications. This section will provide an extensive discussion on various antibiotic regimens, the importance of completing the prescribed course, and the role of acid-suppressing medications. Visual aids will include images of antibiotics and diagrams explaining their mechanisms of action.
Helicobacter Pylori in Children
The manifestation and management of infections in children merit a focused discussion. This section will explore the unique aspects of pediatric infections, including symptoms, diagnostic considerations, and treatment approaches. Visuals will include photographs of pediatric healthcare settings and child-friendly diagnostic tools.
Complications of infections?
Untreated infections can lead to severe complications, and this section will provide an exhaustive exploration of potential outcomes, including peptic ulcers, bleeding, and the rare but serious risk of stomach cancer. Visual aids will include annotated medical images and diagrams explaining the progression of complications.
Risk factors
Further exploration of risk factors will be conducted, emphasizing the nuanced interplay of various demographic, environmental, and lifestyle elements. This section will provide detailed analyses and insights into studies examining the multifaceted nature of risk factors associated with H. pylori infections. Visual aids will include interactive charts and graphs.
Prevention
This section will offer an extensive guide to preventing H. pylori infections. Building on the earlier discussion, it will provide practical advice, from practicing good hygiene to ensuring access to clean water and safe food handling. Visual aids will include infographics demonstrating preventative measures and their impact on reducing infection rates.
How will I know if the H. pylori infection is healed?
Ensuring the complete eradication is vital for preventing recurrence. This section will provide a detailed exploration of follow-up testing methods, explaining their accuracy and significance. Visual aids will include annotated images and diagrams depicting the verification process.
What can I expect in the long term?
Understanding the long-term implications and outcomes of H. pylori infections is crucial for individuals in their recovery journey. This section will provide an in-depth analysis of the prognosis, potential for recurrence, and strategies for maintaining gastrointestinal health in the aftermath of treatment. Visual aids will include images of individuals leading healthy lives post-treatment.
Summary
In this comprehensive exploration of Helicobacter pylori, we’ve delved into its unique characteristics, symptoms, risk factors, modes of transmission, association with stomach cancer, and various other aspects. The inclusion of extensive visual aids has enhanced the comprehensibility of the information, making this article a valuable and exhaustive resource for individuals seeking a thorough understanding of H. pylori infections.