The vagus nerve and its connection to mental health disorders
The vagus nerve is one of the longest and most complex nerves in the human body, playing a crucial role in the communication between the brain and the rest of the body. It is a key component of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates many vital functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. However, recent research has also highlighted the important role of the vagus nerve in mental health disorders.
Understanding the Vagus Nerve
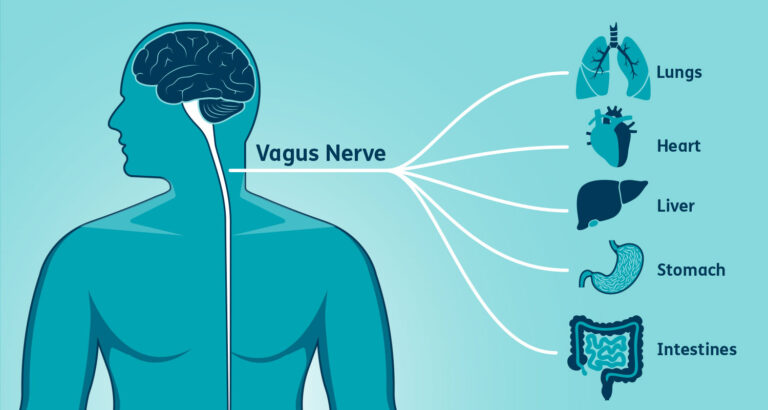
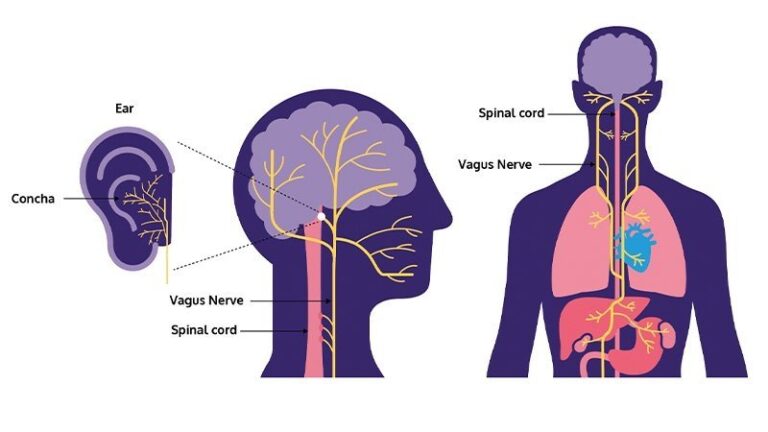
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is a paired nerve that originates in the brainstem and extends down through the neck, chest, and abdomen. It is divided into two branches: the sensory branch, which carries information from the body to the brain, and the motor branch, which carries commands from the brain to the body.
One of the key functions of the vagus nerve is its role in the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for rest and digest functions. When the vagus nerve is activated, it helps to slow down the heart rate, stimulate digestion, and promote relaxation.
The Vagus Nerve and Mental Health Disorders
Research has shown that the vagus nerve also plays a crucial role in mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. The vagus nerve is a major component of the body’s stress response system, known as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. When the body is under stress, the HPA axis is activated, leading to the release of stress hormones such as cortisol.
Studies have found that individuals with depression and anxiety disorders often have impaired vagal tone, which refers to the ability of the vagus nerve to regulate the heart rate in response to stress. Low vagal tone has been associated with an increased risk of developing depression and anxiety disorders.
The Vagus Nerve and Inflammation
Another way in which the vagus nerve may influence mental health is through its role in inflammation. The vagus nerve is known to have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to dampen the body’s inflammatory response. Inflammation has been linked to the development of depression and other mental health disorders, so the anti-inflammatory effects of the vagus nerve may play a protective role.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Given the link between the vagus nerve and mental health disorders, researchers have been exploring the use of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) as a treatment for these conditions. VNS involves the use of a device that delivers electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, helping to regulate its activity.
Studies have shown that VNS can be effective in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety, although the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood. It is thought that VNS may help to regulate the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which are known to play a role in mood regulation.
Conclusion
The vagus nerve is a complex and multifaceted nerve that plays a crucial role in both physical and mental health. Its connection to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety highlights the importance of understanding and studying this vital nerve. Further research into the role of the vagus nerve in mental health could lead to new treatments and therapies for these debilitating conditions.