The Vagus Nerve and Chest Pain: Unraveling the Connection
Chest pain is a symptom that often triggers concern and anxiety due to its association with serious medical conditions, including heart-related issues. However, it may surprise many to learn that the vagus nerve, a key player in the autonomic nervous system, can also be involved in chest pain episodes. In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between the vagus nerve and chest pain, shedding light on the various factors that contribute to this connection.
Understanding the Vagus Nerve:
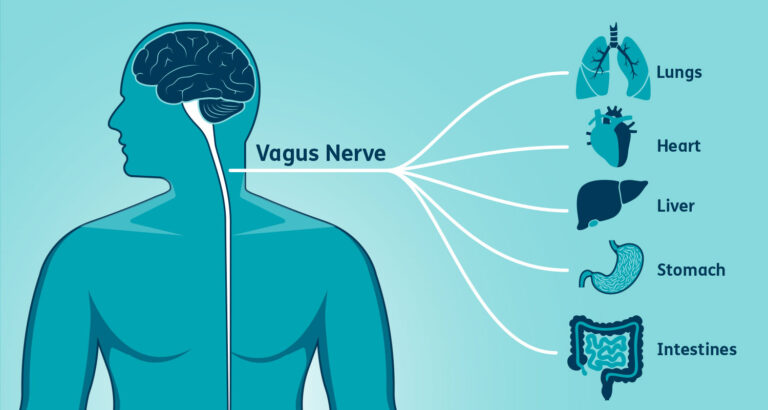
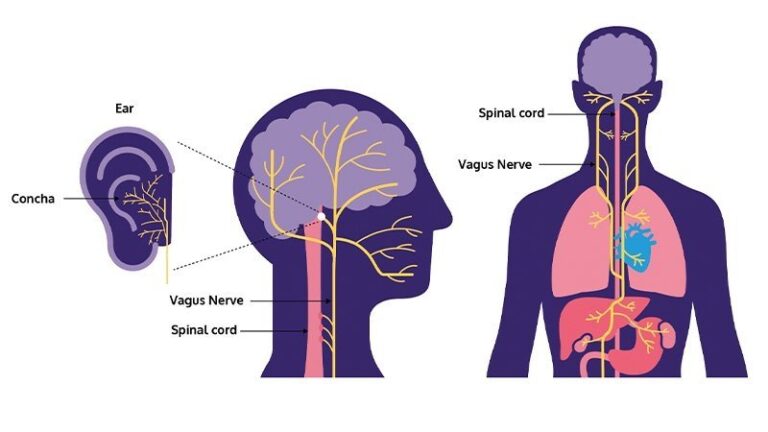
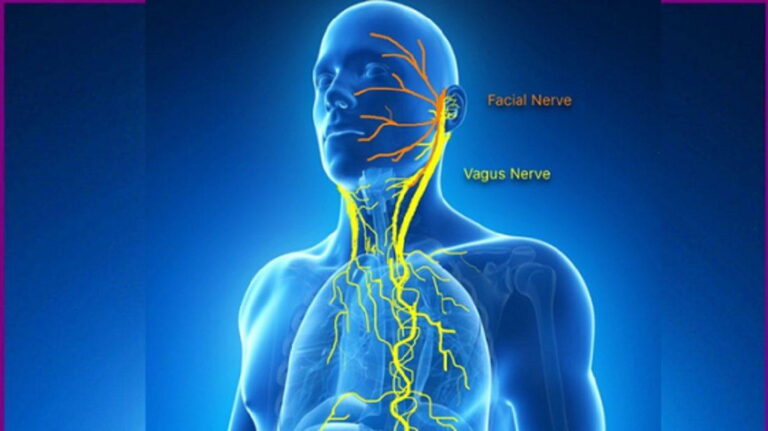
The vagus nerve, or cranial nerve X, is a vital component of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. Its extensive network connects the brain to various organs in the body, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis.
The Vagus Nerve and Chest Pain:
While chest pain is commonly associated with heart-related issues, the vagus nerve can also play a role in certain scenarios. The vagus nerve has branches that innervate the heart, influencing heart rate and rhythm. In some cases, overstimulation or irritation of the vagus nerve can lead to chest pain. This can occur due to:
- Vasovagal Syncope: The vagus nerve is known to induce a response called vasovagal syncope, where stimulation results in a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure. This can lead to fainting and, in some cases, chest discomfort or pain.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: The vagus nerve also innervates the digestive organs, and issues such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can stimulate the vagus nerve, causing chest pain or discomfort.
- Angina Pectoris: Vagus nerve activity can influence blood flow to the heart. In some instances, increased vagal tone may lead to a reduction in blood supply to the heart muscle, contributing to angina pectoris or chest pain.
- Mental Health Factors: Stress and anxiety, which are known to activate the vagus nerve, can contribute to chest pain. The mind-body connection is intricate, and emotional stress can manifest physically, including in the form of chest discomfort.
Management and Precautions:
- Medical Evaluation: If you experience chest pain, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention to rule out serious cardiac conditions. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional can help determine the cause of the chest pain.
- Vagus Nerve Regulation Techniques: Techniques that modulate vagus nerve activity, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga, may be beneficial in managing stress-related chest pain. However, these should be explored under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Addressing underlying conditions, such as GERD or anxiety disorders, can help alleviate chest pain associated with vagus nerve stimulation.
Conclusion:
The connection between the vagus nerve and chest pain adds complexity to the understanding of this common symptom. While serious cardiac conditions must be promptly addressed, acknowledging the role of the vagus nerve in certain instances of chest pain highlights the interconnected nature of the body’s systems. Seeking medical evaluation and guidance is essential for a comprehensive approach to managing chest pain and ensuring optimal heart health. Remember, any chest pain should be promptly assessed by a healthcare professional to rule out serious conditions and determine the most appropriate course of action.